2021
ConTRIVEd: A Novel Method of Protein Quantification
A method for quantifying proteins employing a novel ligand and some chemistry woo.
Novel Magnesium-Based Chlorin for Efficient Catalytic Reduction of CO2
Utilisation of CO2 has historically been done via catalytic conversion into methane or syngas. Such a process involves the use of inorganic and potentially environmental-unfriendly metals while the products are also not biodegradable. Much safer alternatives are proposed in this paper. It is discovered that the introduction of trace Mg2+ into a solution of Chlorin A (Figure 1) results in a catalyst capable of reducing CO2 into various polyalcohols, the latter being energy sources for many organisms.
Chemical Frenetics: Party Drugs as Organocatalysts
We have tested a range of recreational drugs as organocatalysts in the Fukovski Combobulation. Most of the tested drugs are detrimental to the reaction, but cocaine shows promise as a catalyst, with the appropriate dosage. The mechanistic roles of these molecules are probed with chemical frenetic measurements and Density Dysfunctional Theory (DDT).
PPG: Personal Protective Groups as a Defence Against Laboratory Carcinogens
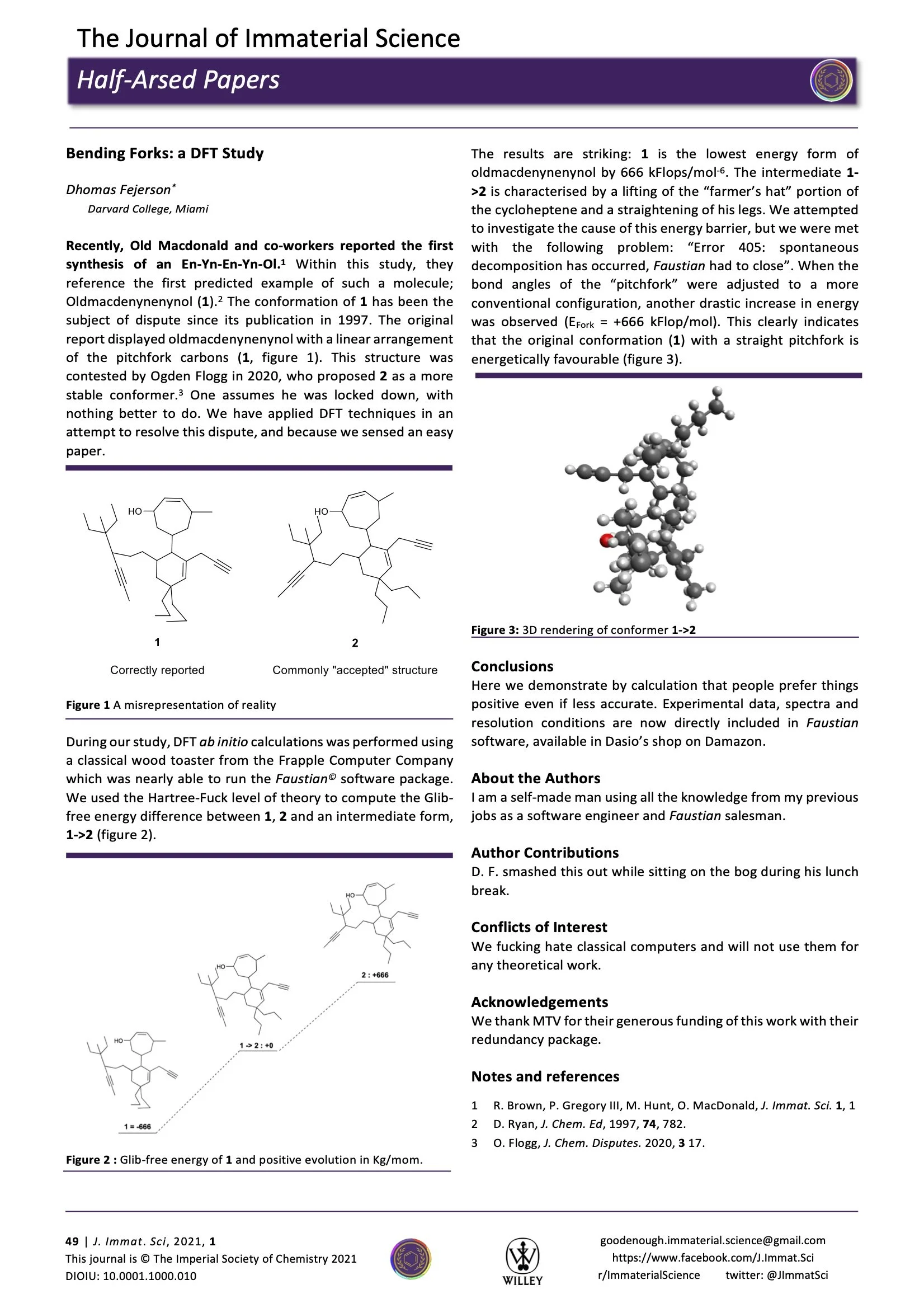
An examination of the conformers of oldmacdenynenynol.
Basketane Carrying Capacity and a Closer Look at the Atom Economy
One can’t judge a book by its cover, but one can judge a reaction by its colour.
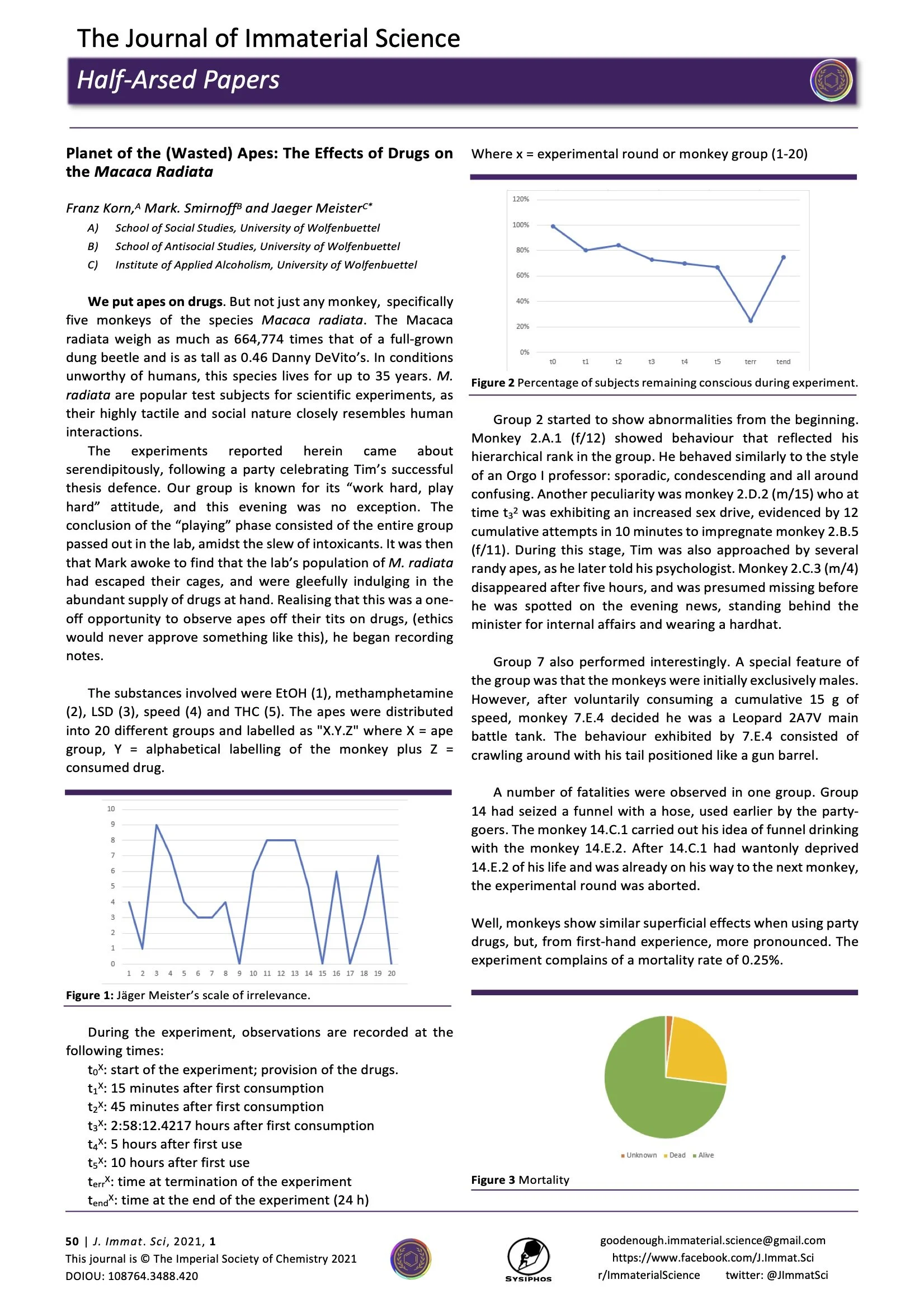
Planet of the (Wasted) Apes: The Effects of Drugs on Macaca Radiata
If you gave an infinite number of monkeys an infinite amount of acid, they might write something like this.
50 Shades of Brown: An Index of Chemical Misery
One can’t judge a book by its cover, but one can judge a reaction by its colour.